Imagine the entire internet as the world’s largest, most chaotic library. Billions upon billions of books (websites), pamphlets (blog posts), and journals (articles) are constantly being added, removed, and updated. Now, imagine someone walks in and asks for “the best chocolate chip cookie recipe” or “affordable plumbers near me.” How does the librarian find exactly what they need in seconds? That librarian is Google’s search algorithm, an astonishingly complex system constantly learning, adapting, and judging. Understanding how it works isn’t just tech trivia; it’s the foundation of being found online. Let’s pull back the curtain on how Google ranks websites.
The Foundation: Crawling, Indexing, and the Quest for Understanding
Before ranking comes discovery. Google doesn’t magically know every page. It relies on digital explorers called Googlebot (its web crawler) to traverse the vast web, following links like paths through a dense forest.
- Crawling: Googlebot starts with known pages and follows links (both internal linking within your site and backlinks from others). Think of it as the librarian’s assistants constantly scouting new publications. If your site is poorly structured, buried under complex code, or blocked by a `robots.txt` file, Googlebot might struggle to find your pages – a critical first hurdle. Ensuring your site is crawlable is step zero.
- Indexing: Once crawled, pages are processed and added to Google’s massive index – a colossal catalog of every known page and what it’s about. This involves analyzing text, images, videos, and code to understand the page’s subject matter (keyword relevance) and purpose. Pages hidden behind login walls or marked `noindex` are excluded from this catalog. Getting indexed means you’re on the shelf, ready to be considered.
- Understanding Search Intent: This is where the magic truly begins. When you type a query, Google doesn’t just match keywords. It strives to understand why you’re searching – your query intent. Are you looking to buy (transactional), learn (informational), find a location (navigational), or discover a specific site (commercial investigation)? Google’s AI in search ranking, powered by systems like BERT and MUM, constantly refines this understanding, analyzing context, synonyms, and the relationships between words. Matching your page’s content to the true search intent behind the query is paramount.
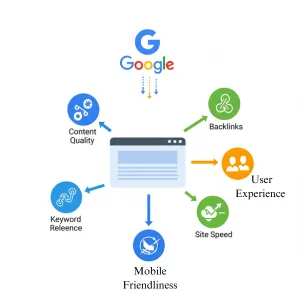
The Ranking Factors:
Once Google understands the query and has relevant pages in its index, the ranking engine kicks in. It evaluates hundreds of signals to order the results on the SERP (Search Engine Results Page). Let’s group the major players:
1. Content: The King (and Queen) of the Realm
- Relevance & Quality: Does your page directly and thoroughly address the user’s query? Surface-level keyword stuffing fails miserably. Google demands content quality, depth, originality, accuracy, and value. Does it answer the question better than competitors? Is it well-organized and readable?
- EEAT: The Trust Imperative (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): This isn’t just a buzzword; it’s Google’s core framework for assessing credibility. Who wrote it? Do they demonstrate real expertise? Is the website an authoritative source on the topic? Is the information accurate and trustworthy? Demonstrating EEAT through author bios, citations, professional design, and transparent information is non-negotiable for competitive topics, especially YMYL (Your Money or Your Life).
- Freshness: For certain queries (news, trending topics, rapidly evolving fields), newer content is favored. However, content relevance and quality often trump sheer newness for evergreen topics.
2. Technical Health: Building a Sturdy Foundation
You can have the world’s best content, but if the library aisle is blocked or the book is falling apart, no one can access it. Technical SEO ensures Googlebot and users can easily navigate and experience your site.
- Page Speed: How fast does your page load? Slow loading times frustrate users and hurt user engagement. Google uses Core Web Vitals (Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, Cumulative Layout Shift) as key speed and interactivity metrics. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights are essential.
- Mobile-Friendliness: With most searches happening on phones, mobile-friendliness is mandatory. Google primarily uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking (mobile-first indexing). A responsive design that adapts seamlessly is key.
- Site Structure & Usability: Is your site logically organized? Clear navigation, a sensible hierarchy (using proper heading tags like H1, H2, H3), and well-implemented internal linking help Googlebot understand your site’s architecture and distribute page authority. Usability for humans – easy navigation, clear calls-to-action – directly impacts user experience (UX).
- Security (HTTPS): A basic ranking signal and essential for user trust. Ensure your site uses a secure connection.
3. Off-Page Signals: Reputation in the Wider Web
What do other sites say about yours? These external endorsements are powerful trust signals.
- Backlinks: Links from other high-quality, relevant websites (backlinks) act like votes of confidence. Not all links are equal; a link from a renowned industry site carries far more weight (domain authority, page authority) than a link from a spammy directory. The quality, relevance, and anchor text of links matter immensely.
- Domain Authority (Conceptual): While not a direct Google metric, the concept of domain authority – the overall strength and trustworthiness of a domain built over time through consistent quality content, technical soundness, and earned backlinks – significantly influences how new pages from that domain are perceived.
4. User Experience & Engagement: The Human Verdict
Google pays close attention to how real people interact with your page in the SERP:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): How often do people click your result when it appears? A compelling, relevant title tag and meta description boost CTR.
- Dwell Time: How long do users stay on your page after clicking? Longer times generally signal that the content is relevant and engaging.
- Bounce Rate: Do users leave immediately without interacting? A high bounce rate can indicate that the page didn’t meet expectations or had poor UX.
- Pogo-Sticking: Do users click your result, quickly return to the SERP, and click another? This is a strong negative signal.
5. Context & Personalization: Tailoring the Results
Google isn’t a one-size-fits-all librarian. It considers context:
- Location-Based Ranking: Searching for “coffee shop”? Your results will prioritize nearby options.
- Search History & Personalization: Past searches and interactions can influence results, though the extent is debated and often subtle for generic queries.
- Device: Results might differ slightly between mobile and desktop.
- SERP Features: Rich snippets, knowledge panels, local packs, and videos can dominate the SERP, pushing traditional “blue links” down. Optimizing for these features is increasingly important.
The Evolving Mind: Algorithm Updates, AI, and Machine Learning
Google’s algorithm isn’t static. It undergoes thousands of changes yearly. Major algorithm updates (like Core Updates, the Helpful Content Update, or Penguin/Panda historically) can significantly reshuffle rankings. These updates often refine how Google assesses content quality, EEAT, user experience, or manipulative tactics like spammy links.
Machine learning in search is fundamental. Systems like RankBrain help interpret ambiguous queries. BERT understands natural language nuances. MUM tackles complex, multi-modal queries. These AI systems continuously learn from vast data, making the algorithm smarter at understanding intent and rewarding truly helpful content.
Actionable Insights:
Understanding these factors isn’t about gaming the system; it’s about aligning your website with what Google (and, more importantly, users) value. Here’s your roadmap:
- Master Search Intent: Before creating content, deeply research the query. What type of result does the user want? Match your content format and depth to that intent.
- Create Exceptional, EEAT-Driven Content: Focus on being the best answer. Demonstrate expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. Be comprehensive, original, accurate, and genuinely helpful. Solve the user’s problem.
- Optimize the Technical Foundation: Ensure your site is fast (page speed), secure (HTTPS), mobile-friendly, and easily crawlable/indexable. Fix technical errors promptly. Use a logical site structure and internal linking.
- Prioritize User Experience (UX): Design for humans. Make navigation intuitive, content scannable, and interactions smooth. A positive user experience keeps people engaged and sends positive signals.
- Earn Quality Links: Focus on creating link-worthy content and building genuine relationships. Avoid manipulative link schemes. Natural, relevant backlinks from respected sources remain powerful.
- Monitor Performance & Adapt: Use Google Search Console and analytics tools religiously. Track rankings, impressions, CTR, traffic, and user engagement metrics. Stay informed about major algorithm updates and adapt your strategy accordingly. Test and iterate.
Key SEO Factor Categories at a Glance
| Factor Category | Core Focus | Key Components | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Quality & EEAT | Creating valuable, trustworthy information | Relevance to search intent, Depth & originality, EEAT demonstration, Accuracy | Directly satisfies user queries and builds trust with Google |
| Technical SEO | Making the site accessible & functional | Page Speed, Mobile-Friendliness, Crawlability, Site Structure, Security | Ensures Google can find and process your content |
| User Experience (UX) | How real people interact with your site | Usability, Navigation, Readability, Dwell Time, Bounce Rate | Engagement signals tell Google your content is useful |
| Off-Page Signals | Reputation & authority signals | Quality Backlinks, Brand Mentions | Acts as external validation of credibility |
The Enduring Truth: Serve the User
Google’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful. Its ranking system is fundamentally designed to reward websites that best fulfill that mission for the specific searcher. While the technical details and weighting of Google ranking factors constantly evolve, the core principle remains: Create genuinely helpful, high-quality content that provides an excellent user experience.
Stop chasing shortcuts and obsessing over manipulating individual signals. Focus instead on understanding your audience’s needs deeply, solving their problems better than anyone else, and building a technically sound, trustworthy online presence. Do that consistently, demonstrate your EEAT, and you’ll find yourself increasingly favored by the world’s most powerful librarian. The SERP awaits.
Ready to put this knowledge into action? Audit your website today. Start with Google Search Console – it’s your direct line into how Google sees your site. Identify your weakest areas (speed? content gaps? mobile issues?) and build a plan to address them. The journey to bette Google search ranking begins with a single step. What will yours be?
Want more local customers to find you? Check out my local SEO package and let’s boost your local visibility today
For any queries, feel free to contact me.



